"'You can foresee all possible situations,'
Bernadette says. And how could I have managed otherwise,
I would like to say to her [...]."1
We have indicated the form of reasoning theorized by Peirce
as the most precious for the progress and creativity of scientific thought. We
will return often to abduction; for the time being we must expand on another
Peircean triad, which is fundamental to understand how the signification process,
the basis of the act of reading, occurs, the first step in an interlingual translation.
In Europe we are used to thinking in Structuralist terms, and to reason
on signification speaking of signifier and signified, following in Saussure's wake.
Saussure has explained that there are many signifier/signified pairs connected in an
arbitrary relation. By "signifier" (signifiant) Saussure means the sound emitted by a
speaker in order to indicate something (for example, the pronunciation of a word),
while by "signified" (signifié) he means the concept the signifier refers to. The
signified/signifier relation is arbitrary, which explains why languages (natural codes)
differ from one another. If, rather, such relation were a necessity, we would have a
single global language, i.e. we would be in a pre-Babel situation. Such relation is
called "signification" (signification).
This theory - at the basis of semiology and Structuralism - explains the
difference between natural codes, but it implies consistency in the signification
relation among speakers of the same code. Moreover, the Saussurian theory is founded
on natural codes, on what are normally called "languages". Research conducted by
Structuralist scientists on other extra-verbal sign systems have the verbal code as a
starting point. Even if linguistics is one of many sign systems considered by semiology,
it is considered as the reference system for all others.
Let us see how semiosis is considered according the sign/object/interpretant
triad devised by Peirce.
Semiosis
(signification process) |
| Peirce |
| A |
sign |
Anything
perceivable: word,
symptom, signal,
dream, letter,
sentence. A sign
stands for an object,
refers to the object.
Without it, it is
impossible to know
the object. |
| B |
object |
What the sign refers
to. It can perceptible
or imaginable. It
determines the sign.
It exists apart from
the sign. |
| C |
interpretant |
Sign, thought
interpreting a
previous sign. Any
new interpretant
throws more light on
the object. |
The sign is anything that can be known,
anything (re)cognizable. But in order for a potential sign
to act as a sign, it has to be related to an object, to be
interpreted and to produce an interpretant in the implied
subject's mind. This interpretive process is called "semiosis".
Here is a graphic representation:
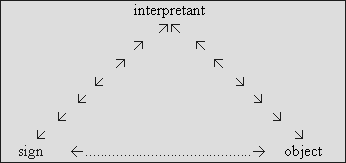
The semiosis triangle according to Peirce
Compared with Saussurian binomial, we notice
that Peircean view leaves room for individual interpretation. The
interpretant is a subjective thought that, for the implied subject
and for her only, refers on one hand to an object, on the other
hand to a sign that is at times used to refer to that object.
That implies that the arbitrariness in Saussurian signification
has in Peirce a subjective dimension which is not arbitrary. For
each of us, the relation between a sign and an object has a definite
sense, is linked to affects, memories, experiences that have to do with
such semiosis. Through Peirce semiosis gains an affective dimension which,
although subjective, for the subject is not arbitrary at all.
For Peirce, a sign is anything, not necessarily a written
or pronounced word, as it is for Saussure. In Peircean semiotics it
is not linguistics extending itself in order to comprehend other types
of codes; it is semiotics that studies all sign systems, including
linguistic systems as well.
That is very important because it gives dynamics to
semiosis. The interpretant - the thought interpreting a sign - can
in turn become a sign, and abductively generate other objects and
other interpretants, which allows, as we shall see, unlimited semiosis.
An object exists independent of a sign, but it is
cognizable only through a sign. On the contrary, a sign is such
only if it is interpreted as a sign. One of the most frequent
misunderstandings in the acquisition of the "interpretant" notion is
to consider it "a person interpreting". In order to avoid such confusion,
it is advisable to remind that the word "interpretant" is a sort of
abbreviation for "interpretant sign". So we shouldn't mistake an
interpretant with an interpreter.
Semiosis is sign interpretation,
|
an action, or influence, which is, or involves,
a cooperation of three subjects, such as a sign,
its object, and its interpretant, this tri-relative
influence not being in any way resolvable into action
between pairs2. |
quoting Peirce. We shall see how this view of
semiosis is helpful while dealing with reading and, more generally,
translation.
Bibliographical references
CALVINO I. If on a Winter's Night a Traveller, translated by William Weaver, London, Vintage, 1998, ISBN 0-7493-9923-6.
GORLÉE D. L. Semiotics and the Problem of Translation. With Special Reference to the Semiotics of Charles S. Peirce.Amsterdam, Rodopi, 1994. ISBN 90-5183-642-2.
PEIRCE C. S. Collected Papers of Charles Sanders Peirce, ed by Charles Hartshorne, Paul Weiss,
and Arthur W. Burks, 8 vol., Cambridge (Massachusetts), Harvard University Press, 1931-1966.
1 Calvino 1998, p. 112.
2 Peirce, vol. 5, p. 484.
|
|

